Buyers Guide
Overview
Buying a trench drain system can seem like a daunting task at first glance. Many factors are involved in choosing a trench drain system. Those factors include traffic load and type, grate classifications and environment. Also, there are many choices such as channel width, channel material, grate material, grate style, type of slope, load class, etc. Grates need to be chosen that will handle any special traffic such as bicycles, shoe heels and wheelchairs. These trench drain choices can lead to analysis paralysis, but taken one by one, choices can be narrowed to highlight the choice that is right for your application. The following information will help answer these questions.
First, a quick discussion about cost. It would be easy to scan a selection of trench drains and just choose the least expensive. As we say, “You only get to pour the concrete once…”. Quality trench drain systems suited for the correct purpose can be expensive. The consequences of choosing an inadequate trench drain can also be expensive because if the drain deteriorates it can become unsightly and may need to be replaced sooner than anticipated. On the flip side, over engineering the trench drain either by installing a larger drain than needed or higher grade than needed can be a waste of resources. Here at Trench Drain Supply we carry all of the major manufacturers and strive to help our customers purchase the correct trench drain system for their project requirements. Since we specialize in trench drains and know the ins and outs of each manufacturer, we can find the correct product for your application at the best price.
When calling our sales team for a quote, we have a series of questions we ask to narrow down the direction we need to take in order to choose the best system and quote for your application. Let’s walk through these steps.
- Is this a new install or do you need replacement parts? (If replacement parts are needed, please check out the Grate Guy page on this website.)
- Where will the trench drain system be installed? Public or private, residential or commercial?
- What is the expected grade load class? Load Class A, B, C, D, E, or F?
- Will pedestrians be using this application? Should it be ADA compliant, heel-proof safe, bicycle safe, or have a detectable grate?
- How long a run will be required? How wide?
- Is the bed sloped or is a pre-sloped channel needed? What is the longitudinal pavement slope?
- What materials are most applicable for the system such as concrete or asphalt or pavers?
- Will any unusual chemicals be drained?
- Are there any catch basin or extra outlet requirements?
- What is the outlet type? Vertical, horizontal, In-line catch basin, or catch basin.
Basic Concepts and Terminology
Purpose
The purpose of a trench drain system is to protect against damage to paved surfaces and surrounding areas related to water or chemical runoff. Systems consist of a trough or channel-shaped body which is used for the rapid evacuation of surface water or chemical spills.
Trench Drain System Categories
- Residential - These trench drain products are for homeowners and light duty projects.
- Commercial - These trench drain products are for businesses and heavy duty applications.
- Heavy Duty - These trench drains are designed for large water flow and/or heavy equipment.
- Shallow - This drain is a specialty drain used in areas where height and installation depth are an issue. Regular trench drains run from around 4 1/2” deep to upwards of 17” deep. Shallow trench drains run from 2 1/4” to 3 1/2’ deep. Because of the height restrictions, shallow trench drains do not come in pre-sloped.
- Stainless Edge - These drains are hygienic, do not rust, and are easy to clean so they are great for use in kitchens and baths.
- Shower - Drains used in the construction of showers and baths are an exciting area of home improvement. They can give a tile shower enclosure a nice modern feel.
- Pool - Pool drains are typically made of plastic and have no metal. They are usually narrower than regular trench drains, have decorative plastic or aluminum grates and come in various widths.
Trench Drain Parts
The general parts of a trench drain system are:
- Solid End Cap - These caps are attached to the end of the channel that have no opening to prevent water leakage.
- Grate - A grate covers the channel and provides a surface for vehicles, bicycles, and pedestrians. Grates have classifications depending on the application.
- Bottom Outlet - The bottom outlet has an opening that allows for drainage of the water from the channel.
- End Outlet Cap - End outlet caps are attached to the end of the channel and have an opening for water drainage.
- Channel - The channel is a manufactured bed that directs water flow.
There are two kinds of channels: neutral (no fall) and pre-sloped (linear fall).
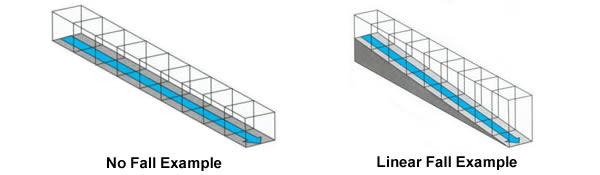
Every make and model comes in neutral, but not all types have a pre-sloped option. Pre-sloped means that the bottom of the trench drain becomes gradually deeper as the run progresses. This is very effective at driving the water downhill to the outlet or in the direction desired. This is achieved by making each channel in the trench drain run differently. Each channel has a number from 1 (the most shallow) to 10 (or 25 or 30 or 40) and must be installed as a series. Neutral channels have no slope and are a set depth with the bottom of the trench drain channel being the same depth on either end of the run. Water will flow to the outlet on a natural basis. These channels are used in shallow applications or where there is a sloped bed. Neutral channels can be combined with pre-sloped channels in a series to provide a run with desired results. They are easier to install because they can be installed in any order and easily accommodate any corners or connections.
Channels also come in a variety of width classes.

Manufacturers quote width in different ways. Some quote the width from the interior of the channel, some quote width from the exterior of the channel, and some quote the total “reveal” of the trench drain channel. What really matters is how much water can be moved. Trench Drain Supply has broken channel widths into classes to simplify this confusion. The classes are 2”, 3”, 4”, 6”, 8”, 12” and Over 12”. Putting them into classes gives the consumer an apples-to-apples ability to compare trench drain channels with similar characteristics.
Grate Locks - Grate locks secure the grate to the channel with locks or connectors. These differ depending on manufacturer.

Wheelchair Accessability requires all grates follow ADA guidelines for safety and accessability. Wheelchairs should be able to manuveur over grating systems without difficulty.

Heel Proof means that a grate must not cause falls in pedestrian traffic. High heel shoes, which could get stuck in average grates, must be considered. Grates that have openings from 1/4” to 5/16” can be used to accommodate shoes with high heels.
Bicycle Traffic requires grates to be engineered and installed so that a bicycle wheel may not fall into a slot in the grate causing a crash. Replace existing grates (See A and B in figure below) or weld thin metal straps across the grate perpendicular to the direction of traffic (See C in figure below) is required. These should be checked periodically to ensure that the straps remain in place. Make sure that grates installed for bicycle traffic are installed flush with the road surface.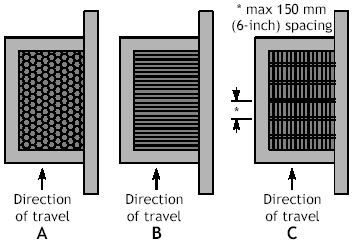
SHARED ROADWAYS FHWA COURSE ON BICYCLE AND PEDESTRIAN TRANSPORTATION, Section 18.8
FDOT Drainage Considerations for Bicycle & Pedestrian Facilities
Decorative grates that will add architectural detail and design should be considered.
Hygienic grates are stainless steel grates and are the perfect choice for hygiene in locations such as kitchens and baths. Stainless steel will not rust or corrode and is easily cleaned.
Standards and Guidelines
There are several organizations that set the standards or guidelines for trench drain systems.
DIN (Deutsches Institut fur Normung E.V.) German Institute for Standardization is the German national organization for standardization. DIN19580 is the only standard written specifically for trench drains and is internationally recognized. Current DIN/EN Load Classifications for trench drain grates are:
- A: Up to 3,372 pounds for pedestrians and cyclists.
- B: Up to 28,100 pounds for sidewalks, pedestrian areas and small parking lots.
- C: Up to 56,200 pounds for parking lots and general commercial use.
- D: Up to 89,920 pounds for roads and highways.
- E: Up to 134,800 pounds for industrial areas, gas stations, and loading dock facilities.
- F: Up to 202,320 pounds for airports and docks.
EN European Norms European Standards are specifications defining requirements for products, production processes, services or test-methods. These specifications are voluntary. They are developed by industry and businesses following some basic principles such as consensus, openness, transparency and non-discrimination. Specifications ensure compatibility and safety, reduce costs and help companies join in trade. European Standards are under the responsibility of the European Standardisation Organisations (CEN, CENELEC, ETSI). EN works in conjunction with DIN.
AASHTO American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials is a nonprofit, nonpartisan association representing highway and transportation departments in the United States. It represents five transportation modes: air, highways, public transportation, rail and marine. ASHTO has set standards for all phases of highway system development. Standards are issued for design, construction of highways and bridges, materials, and other technical areas.
ASME The American Society of Mechanical Engineers is a not-for-profit membership organization that enables collaboration, knowledge sharing, career enrichment, and skills development across all engineering disciplines, toward a goal of helping the global engineering community develop solutions to benefit lives and livelihoods. Standard A112.6.3 This Standard covers floor, area, adjustable floor, and trench drains that are used inside of, or outside and immediately adjacent to, building structures. This Standard specifies design requirements, definitions, nomenclature, outlet types and connections, grate-free area, top loading classifications, materials and finishes. Seam welded, socket type, stainless steel fabricated drains are covered in ASME A112.3.1.
Drain Standards A112.6 6.1 Loading Classifications Grates and top rims shall be designed to meet the following loading classifications:
- 6.1.1 – Light Duty - All grates having safe live load (as calculated in para. 6.2.5) under 2000 pounds.
- 6.1.2 – Medium Duty - All grates having safe live load (as calculated in para. 6.2.5) between 2000 pounds and 4999 pounds.
- 6.1.3 – Heavy Duty - All grates having safe live load (as calculated in para. 6.2.5) between 5000 pounds and 7499 pounds.
- 6.1.4 – Extra Heavy Duty - All grates having safe live load (as calculated in para. 6.2.5) between 7500 pounds and 10,000 pounds.
- 6.1.5 – Special Duty - Grates having safe live load (as calculated in para. 6.2.5) over 10,000 pounds shall be considered special and treated accordingly.
Heel-proof Standard ASME A112.6.3-2016 [Revision of ASME A112.6.3-2001 (R2007)] Floor and Trench Drains
ANSI American National Standards Institute A private, non-profit organization that administers and coordinates the U.S. voluntary standards and conformity assessment system. This organization works with different entities to identify and develop standards for goods and services. ANSI works closely with ASME.
- All grates having safe live load (as calculated in paragraph 6.1.6 of the ANSI Standard) under 2,000 pounds are for pedestrian foot traffic only.
- All grates having safe live load (as calculated in paragraph 6.1.6 of the ANSI Standard) between 2,000 pounds and 4,999 pounds are for light pneumatic tire traffic, sidewalks, and residential parking.
- All grates having safe live load (as calculated in paragraph 6.1.6 of the ANSI Standard) between 5,000 pounds and 7,499 pounds are for Commercial Pneumatic tire traffic patterns and tractor trailers.
- All grates having safe live load (as calculated in paragraph 6.1.6 of the ANSI Standard) between 7,500 pounds and 10,000 pounds are for forklift traffic, roads and highways H-20 load rated.
- All grates having safe live load (as calculated in paragraph 6.1.6 of the ANSI Standard) over 10,000 pounds are for airport traffic.
ADA American Disabilities Act is a civil rights law that prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities in all areas of public life, including jobs, schools, transportation, and all public and private places that are open to the general public. 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design 302.3 Openings. Openings in floor or ground surfaces shall not allow passage of a sphere more than 1/2” (13 mm) diameter except as allowed in 407.4.3, 409.4.3, 410.4, 810.5.3 and 810.10. Elongated openings shall be placed so that the long dimension is perpendicular to the dominant direction of travel.
Federal Government Standards (RR-F-621C) Strength Criteria for Cast Iron Items In Highway Drainage Structures This government publication discusses the standards and strengths of manholes and grates on highways.
Live Load Ratings
AASHTO's H-20 and HS-20 are live load ratings applied to the design of bridges or other suspended items (e.g., lids for concrete drains). H signifies 2 axial trucks weighing 20 tons; HS signifies 2 axial trucks with semi. An informative article on live load ratings can be found here: Live Load Ratings.
